Version upgrade¶
Considerations¶
Upgrading to Zentyal 7.1 must be performed from a Zentyal 7.0 fully updated. Versions prior to 7.0 must be upgraded progressively. The complete upgrade sequence from Zentyal 3.2 version is as follows:
3.2 -> 4.x -> 5.x -> 5.x -> 6.0 -> 6.1 -> 6.2 -> 7.0 -> 7.1.
Warning
These instructions are valid for upgrading from version 7.0 Development Edition to 7.1. For a Commercial Edition, you must contact the Support Team. If you do not have access to the Support Portal [1] you must contact the Zentyal Team [2] to request access.
| [1] | Support Portal: https://zentyal.atlassian.net/servicedesk/customer/portal/4/ |
| [2] | Contact: https://zentyal.com/contact-us/ |
Before starting with the upgrade, we strongly recommend to perform a series of preliminary checks to try to minimize prior checks to try to minimize possible issues. These checks are detailed in the following section.
It is of vital importance to have a backup of the server before proceeding with the upgrade. The upgrade is a complex process and can fail leaving the system damaged or even unrecoverable.
Warning
Please remember that a configuration backup is not a full backup as detailed here [3].
| [3] | Configuration backup: https://doc.zentyal.org/en/backup-conf.html |
Pre-update¶
The following are the actions to be checked prior to the upgrade.
Log errors¶
One of the most important tasks is to confirm that the most critical system log files are free of errors. The minimum files to check are:
/var/log/zentyal/zentyal.log/var/log/syslog
Disk space¶
As this is a minor upgrade, the required disk size is reduced. If the operating system does not have system has no pending updates, less than 200MB will be sufficient:
df -h
Internet access¶
In order to download the packages needed to perform the upgrade, the server must have Internet access:
ping -c5 google.com
Access to the repositories¶
Another critical task to check is the access to Ubuntu and Zentyal repositories. To do so, just run the following command to confirm that there are no errors:
sudo apt update
Available packages¶
To check if the operating system is up to date, we will have to execute the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt list --upgradable
Broken packages¶
It is imperative that we check for any broken packages, otherwise, the update will fail.
dpkg -l | egrep -v '^(ii|rc)'
In case of broken packages, the Troubleshooting section [4] explains how to try to fix them.
| [4] | Troubleshooting: https://doc.zentyal.org/en/upgrade.html#id15 |
Database errors¶
Another important task is to check if there are any errors in the MySQL hosted databases used by Zentyal for its modules:
mysqlcheck -u root -p$(sudo cat /var/lib/zentyal/conf/zentyal-mysql.passwd) --all-databases 2> /dev/null
In case of using the [5] domain controller module, it is also highly recommended to confirm its status:
sudo samba-tool dbcheck --cross-ncs
In case of detecting an error in this last database, we will have to follow [6] this link.
| [5] | Domain Controller: https://doc.zentyal.org/en/directory.html |
| [6] | Documentation on the Samba database: https://wiki.samba.org/index.php/Dbcheck |
System report¶
We can obtain the results of the checks mentioned in this section and much more information by generating a system report [7] and analyzing it before scheduling the server upgrade.
| [7] | System report: https://doc.zentyal.org/en/smart-admin.html#system-status-reports |
Update¶
Once we have reviewed your system and confirmed that it is stable, we can proceed with the upgrade. We have two options to carry out the upgrade:
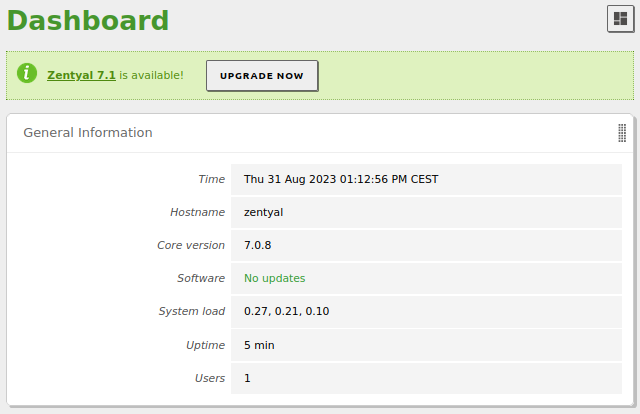
1. Upgrade the system by clicking on the Upgrade button available on the Webadmin.
Warning
If the server does not have an Internet connection, the button will not be displayed.
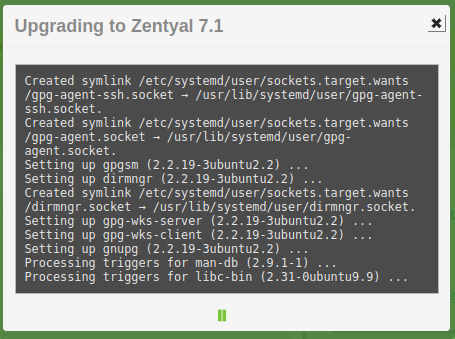
Once we start the upgrade, we will see the process in a modal window.
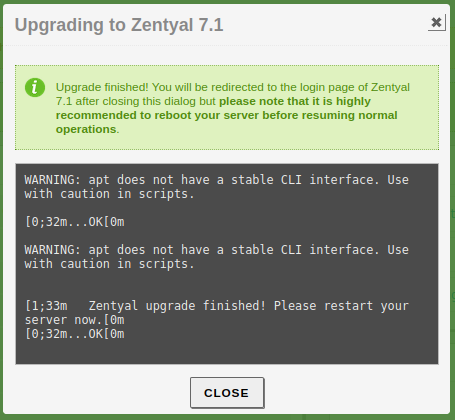
When the upgrade finishes, we should see a success or failure message.
Warning
If we do not get any of those messages, the web browser session might have expired, so we will need to check in
the log file /var/log/zentyal/zentyal.log. If the upgrade has finished, just refresh the page.
2. From the command line (recommended option to detect errors in the process):
sudo bash -x /usr/share/zentyal/release-upgrade
Warning
The terminal from which the command is being executed cannot be closed until the process has finished.
Tip
A good practice is to store the output generated by the script in a text file in case it is necessary to analyze it in detail.
Post-update¶
Once the upgrade has finished, we will need to check the following before restarting the server.
1. That the Ubuntu version is still 20.04:
lsb_release -a
2. That the Zentyal packages have been upgraded to 7.1:
dpkg -l | egrep 'zen(tyal|buntu)-': :: dpkg -l | egrep 'zen(tyal|buntu)-'
3. That there are no broken packages:
dpkg -l | egrep -v '^(ii|rc)'.
If all of the above is correct, we can proceed to restart the server.
4. Once it has started, we will analyze the following log files to confirm that no errors have occurred:
/var/log/zentyal/zentyal.log/var/log/syslog.
5 Finally, we will check the operation of each module to make sure that it is stable after the upgrade.
Troubleshooting¶
In the event that the upgrade has failed, we must identify the point at which the server is where the server is before considering restoring a backup.
Current server status¶
To confirm the status of the server after the failure during the upgrade, the questions we should ask and try to answer are:
- 1. Was the Ubuntu version upgraded to a version other than 20.04? If the answer is yes,
- you will have to restore a backup, since Zentyal 7.1 is based on Ubuntu 20.04.
- 2. Have any Zentyal module ever been updated? If no module was upgraded and there are no broken packages
- packages are broken, in principle only read-only runs were performed, so it should not be necessary to restore a backup. it should not be necessary to restore a backup copy.
- 3. Are there any broken packages? If there are any broken Zentyal packages, with the help of the logs you could recover them
- and finish upgrading the server without any problems. If there are any broken packages, with the help of the logs you could recover them and finish upgrading the server without the need to restore a backup.
4. What errors are seen in the log files? NOTE: You should also check the file /var/log/log/dpkg.log.
Broken packages¶
If you have broken packages, you can try to fix them with the following commands.
To fix all the packages at once:
sudo dpkg --configure -a
Warning
It may be necessary to run the command multiple times
In case this does not work, you will have to do it package by package:
sudo dpkg --configure name_of_the_package
Warning
You may have to repeat this several times to fix all the packages.