Mail filter¶
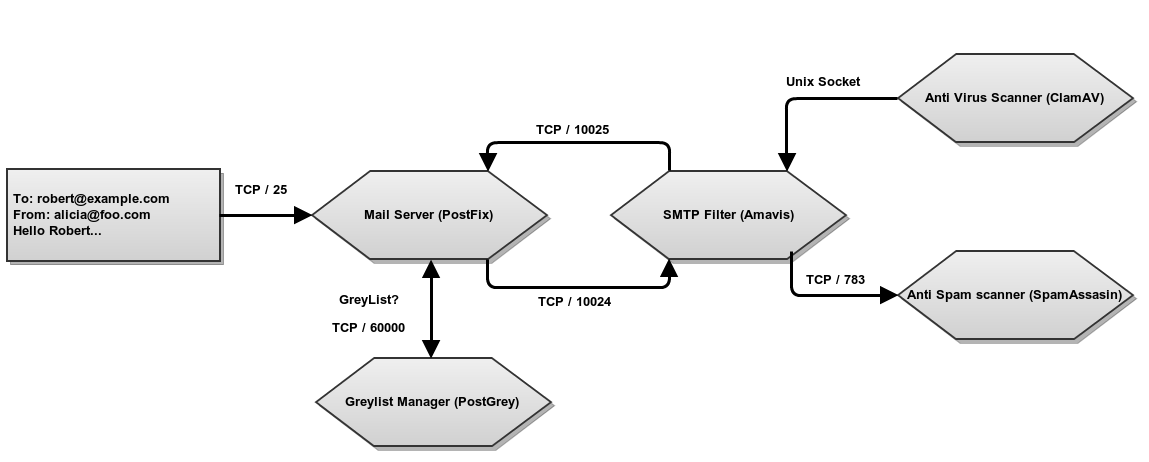
Mail filter schema in Zentyal¶
Zentyal offers a powerful and flexible mail filter to defend your network and users from these threats.
In the figure, you can see the different steps an email passes through before being tagged as valid or not. First, the email server sends the message to the greylisting policies manager where, if considered as potential spam, it will be rejected and the system requests that the message is to be forwarded to the source server. If the email passes through this filter, it will go to the mail filter. This will use a statistical filter to check a series of email features to discover whether it contains virus or is junk mail. If the email passes through all the filters, it is considered valid and it is sent to the recipient or stored on the server’s mailbox.
In this section you will find a detailed explanation of each of these filters and how they are configured in Zentyal.
Greylist¶
The greylists [1] take advantage of the expected behaviour of a mail server dedicated to spam. The behaviour helps to discard or accept the received emails or, at least, make it difficult to send them.
Servers dedicated to spam are optimised to send as many emails as possible in minimum time. To do this, the messages are auto-generated and then directly sent, without caring about whether they are received or not. When you have a greylist system, the emails considered as potential spam are rejected and the mail server is asked to send the email again. If the server is actually a spammer server, it probably doesn’t have the necessary tools to manage this request and therefore, the email will never reach the recipient. On the contrary, if the email was legitimate, the sending server will simply re-send mail.
The Zentyal strategy is to pretend to be out of service. When a new server sends an email, Zentyal responds “I am temporarily out of service” during the first 300 seconds [2]. If the sending server complies with the request, it will re-send the email after this time and Zentyal will mark it as a valid server.
In Zentyal, the greylist exempts mail sent from internal networks, mail sent from objects with a policy of allowing retransmission and those whose sender is an address that is on the antispam whitelist.
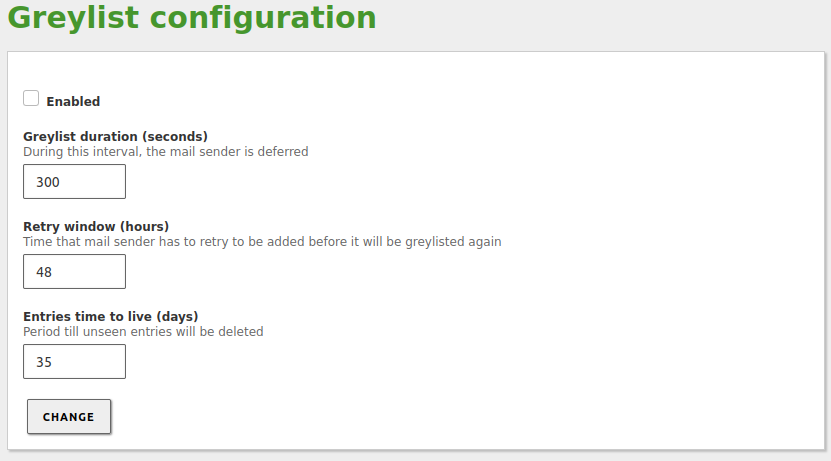
The Greylist is configured via with the following values:
- Enabled:
- Click to enable greylisting.
- Greylist duration (seconds):
- Seconds the sending server must wait before re-sending the email.
- Retry window (hours):
- Time in hours in which the sending server can send mail. If the server has sent any mail during this time, this server will go to the greylist. In a greylist, the mail server can send as many emails as it wants without time restrictions.
- Entry time-to-live (days):
- Number of days during which the data of the evaluated servers will be stored in the greylist. Once the configured days have gone by without the sending server to be seen, when the server sends email again, it must go through the greylisting process described above.
| [1] | Zentyal uses Postgrey (http://postgrey.schweikert.ch/) as a Postfix policy manager. |
| [2] | Actually the mail server responds “Greylisted”, i.e. moved to the greylist and pending to allow or disallow the mailing once the configured time has passed. |
Content filtering system¶
Email content filtering is processed by the antivirus and spam detectors. To carry out this task, Zentyal uses an interface between the MTA and these applications. To do this, the amavisd-new [3] application is used to ensure that the email is not spam and it does not contain viruses.
In addition, amavisd carries out the following checks:
- Blacklists and whitelists of files and extensions.
- Mail filtering of emails with malformed headers.
| [3] | Amavisd: http://www.ijs.si/software/amavisd/ |
Antivirus¶
Zentyal uses the ClamAV [4] antivirus, an antivirus toolkit especially designed to scan email attachments in a MTA. ClamAV uses a database updater that allows the scheduled updates and digital signatures through the Freshclam program. This database is updated daily with the new viruses that are found. Furthermore, the antivirus is capable of native scanning of a number of file formats, such as Zip, BinHex, PDF and so on.
It is optional to install the antivirus module, but if you do install it, you can see that it integrates with some Zentyal modules. This integration increases the security of the configuration options of different services such as the SMTP filter, File sharing or the HTTP proxy.
| [4] | ClamAV: http://www.clamav.net/ |
Antispam¶
The antispam filter gives each email a spam score. If the email reaches the spam threshold, it is considered junk mail and if not, it is considered as legitimate email. The latter kind of email is often called ham.
The spam scanner uses the following techniques to assign scores:
- Blacklists published via DNS (DNSBL).
- URI blacklists that trac antispam websites.
- Filters based on the message checksum, checking emails that are identical, but with some few changes.
- Bayesian filter, a statistical algorithm that learns from its past mistakes when classifying an email as spam or ham.
- Static rules.
- Other. [5]
Zentyal uses SpamAssassin [6] as spam detector.
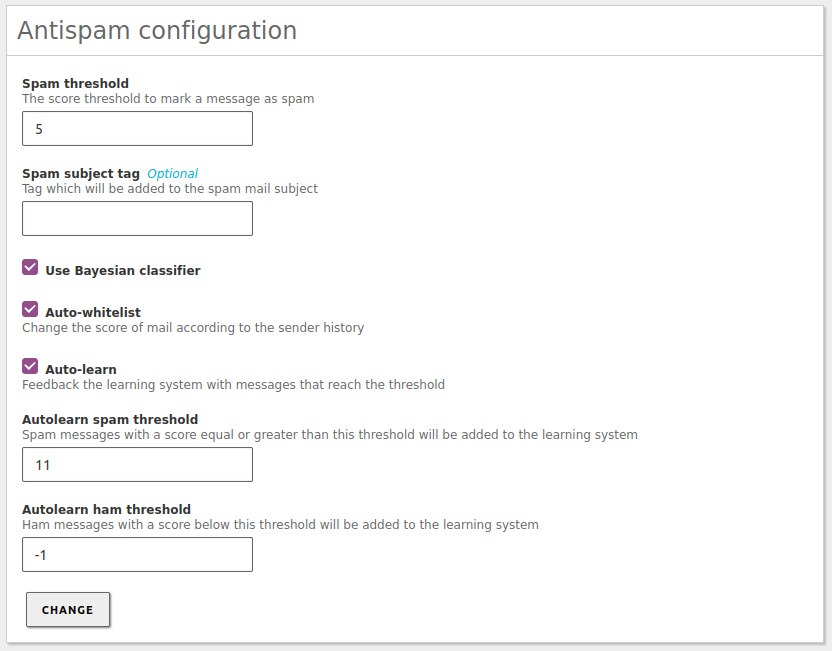
The general configuration of the spam filter is done from .
- Spam threshold:
- Mail will be considered spam if the score exceeds this value.
- Spam subject tag:
- Tag to add to the mail subject in case it is spam.
- Use Bayesian classifier:
- If marked, Bayesian filter will be used. Otherwise it will be ignored.
- Auto-whitelist:
- Considers the account history of the sending server when giving the score to the message. If the sender has sent plenty of ham emails, it is highly probable that the next email will be ham and not spam.
- Auto-learn:
- If marked, the filter will learn from the received messages, which score exceeds the auto-learn thresholds.
- Autolearn spam threshold:
- The filter will learn that email is spam if the score exceeds this value. You should not set a low value, since it may cause false positives. The value must be greater than the Spam threshold.
- Autolearn ham threshold:
- Filter will learn that email is ham if the score is below this value. You should not set a high value, since it may cause false negatives. The value must be less than 0.
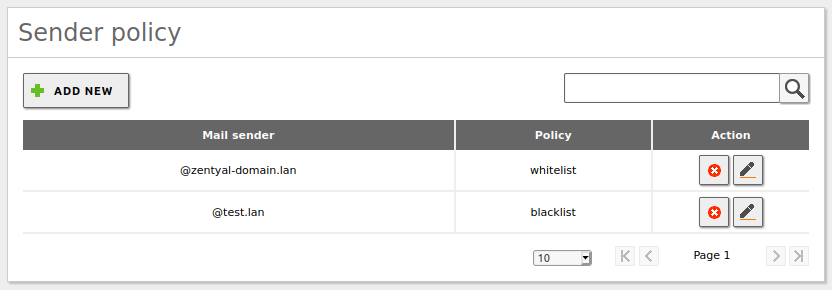
From Sender Policy, you can configure senders whose emails are always accepted (whitelist), always marked as spam (blacklist) or always processed by the antispam filter (process). If a sender is not listed here, the default behaviour is to filter.
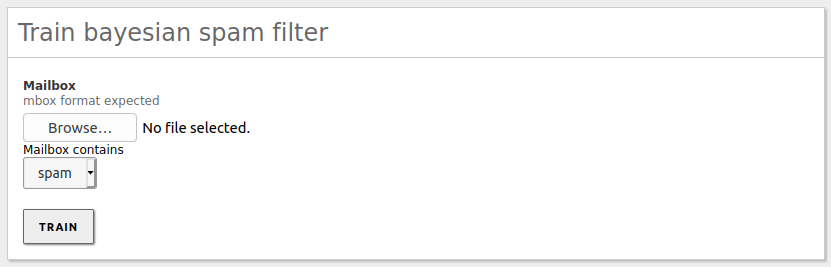
From Train Bayesian spam filter, you can train the Bayesian filter by sending it a mailbox in Mbox [7] format, containing only spam or ham. You can find many sample files from the Internet to train the Bayesian filter, but usually you get more accurate results if you use email received from the sites you need to protect. The more trained the filter is, the better results you get when testing if a message is junk or not.
| [5] | Antispam techniques: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anti-spam_techniques_(e-mail) |
| [6] | SpamAssasin: http://spamassassin.apache.org |
| [7] | Mbox and maildir are email storage formats, independent of the used email client. In Mbox, all the emails are stored in a single file, whilst maildir organises emails into separate files within a directory. |
SMTP mail filter¶
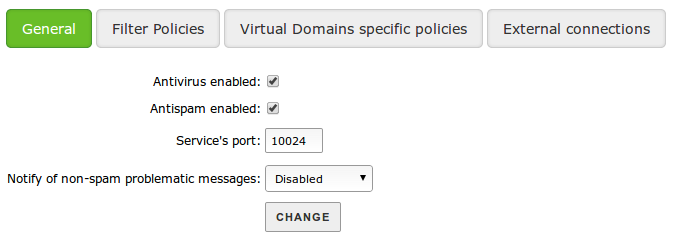
From , you can configure the behaviour of the previously mentioned filters when Zentyal receives mail by SMTP. From , you can configure the general behaviour of all incoming mail:
- Enabled:
- Check to enable SMTP filter.
- Antivirus enabled:
- Check to ensure the filter searches for viruses.
- Antispam enabled:
- Check to ensure the filter searches for spam.
- Service port:
- Port to be used by the SMTP filter.
- Notify of non-spam problematic messages:
- You can send notifications to a mailbox when you receive problematic emails that aren’t spam, for example, emails infected by a virus.
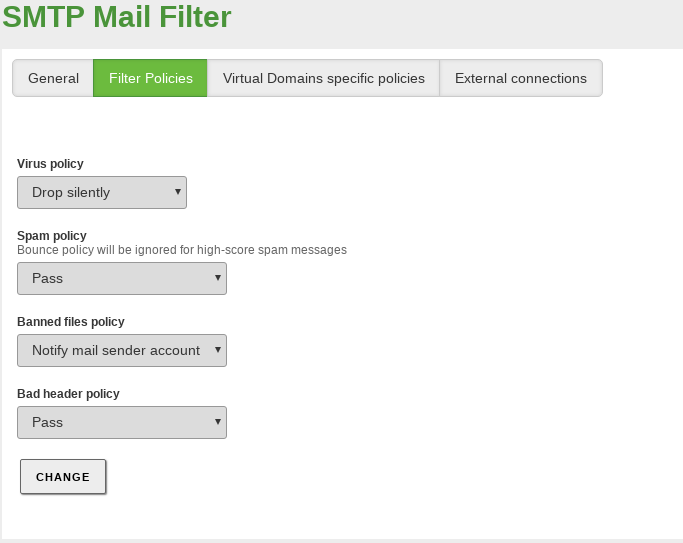
From , you can configure how the filter must act with different types of emails.
You can perform following actions with problematic emails:
- Pass:
- Don´t take any special action and let the email reach its recipient. Nevertheless, in some cases (like spam or virus), the mail server will add a warning to the email subject.
- Notify mail sender account:
- Discard the message before it reaches the recipient and notify the original sender account that the message has been discarded.
- Notify sender server:
- Discard the message before it reaches the recipient and notify the server of the sender account. It’s very common that the sending server then notifies the user about this with an automatic Undelivered Mail Returned to Sender message.
- Drop silently:
- Discard the message before it reaches the recipient without notifying the sender or the sending server.
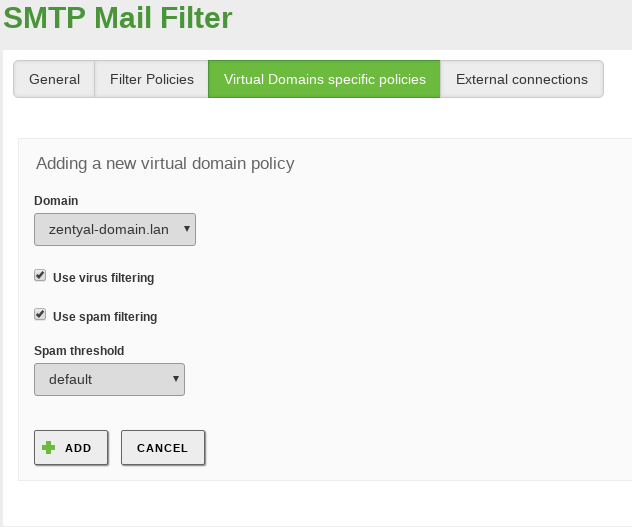
From tab, you can configure the filter behaviour for virtual domains of the email server. These settings override the previously defined default settings.
To customise the configuration of a virtual mail domain, click on Add new.
The parameters that can be overridden are the following:
- Domain:
- Virtual domain you want to customise. Those configured in are available.
- Use virus / spam filtering:
- If enabled, the email received in this domain will be filtered in search of viruses or spam.
- Spam threshold:
- You can use the default score for spam or a custom value.
Once you have added the domain, you can add addresses to your whitelist, blacklist or force the processing from .