Virtualization Manager¶
Zentyal offers easy management of virtual machines by integrating the KVM [1] solution.
| [1] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel-based_Virtual_Machine |
Creating virtual machines with Zentyal¶
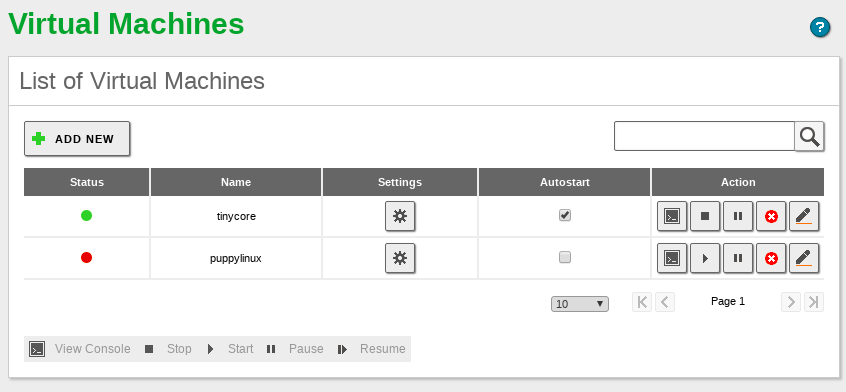
Through the menu you can access the list of currently available machines, as well as add new ones or delete the existing ones. You also have other maintenance options that will be described in detail in the next section.
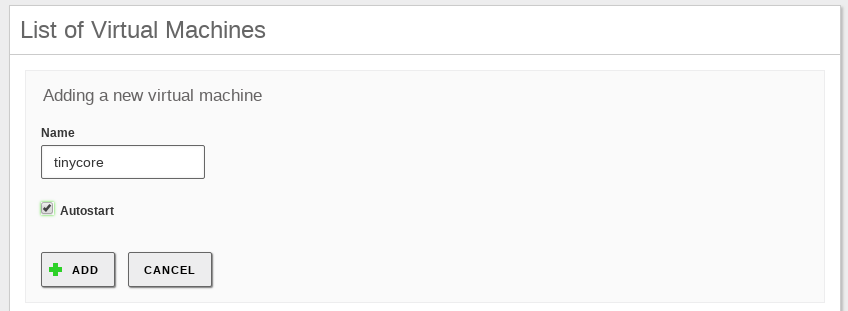
When you create a machine, you have to click in Add new and then fill the following parameters:
Name
Just for identification purposes, it will also be used to pick the file system path where you will store the data associated with this machine, but essentially, you can enter any alphanumeric label.
Autostart
If this option is enabled, Zentyal will be in charge of starting or stopping the machine along with the rest of the services, otherwise Zentyal will just create the machine the first time you configure it and save changes. The system administrator will be in charge of performing these actions manually when he/she considers necessary.
After this, you have a configuration row associated with your new machine.
The next step will be configuring your new virtual machine, through the Settings column, where you will find the following tabs:
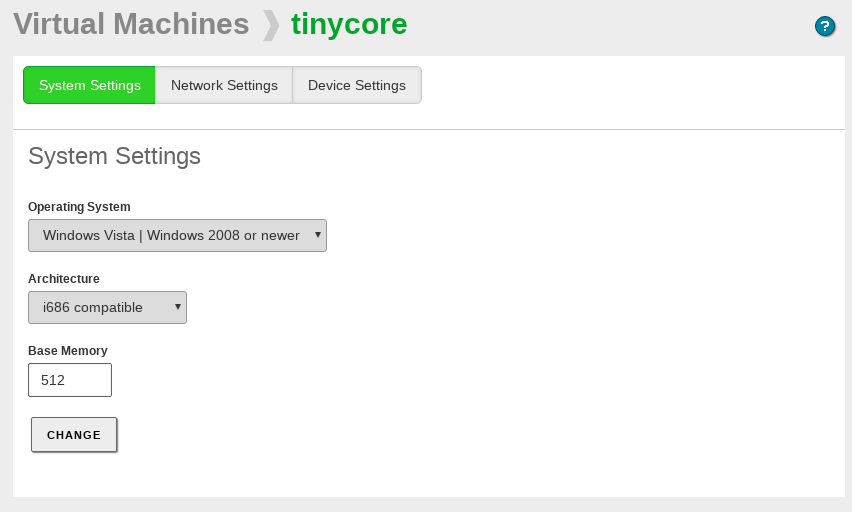
System Settings
It allows you to define the architecture (32 or 64 bits). You can also define the size of the RAM memory allocated for this machine in megabytes. By default this value is 512, or half the available memory if you have less than 1GB in the real host.
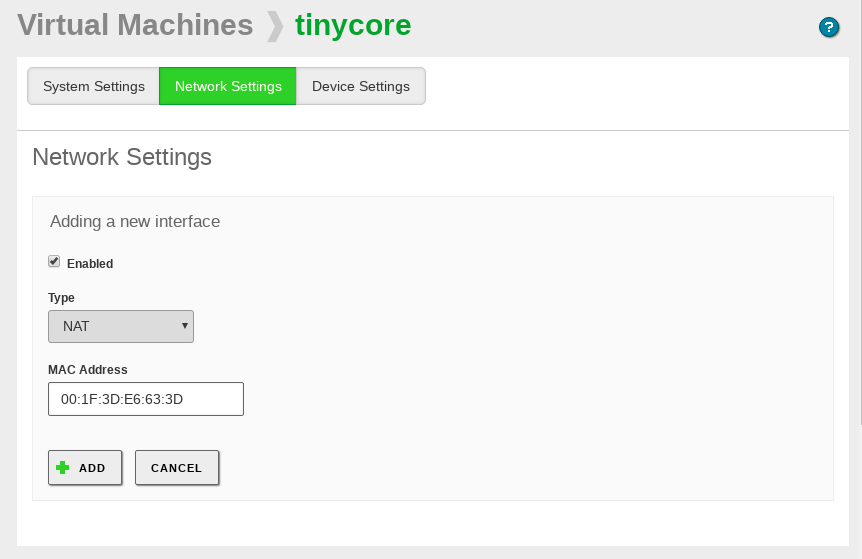
Network Settings
It contains the list of network interfaces of the virtual machine, which can be configured as NAT (only Internet access), in bridged mode with one of the host system interfaces or forming an isolated internal network, which name you have to define, so other virtual machines will be able to connect. If you uncheck the Enabled checkbox, you can temporally disable any of the configured network interfaces. As you can see below, it is possible to modify also the MAC address associated to this interface.
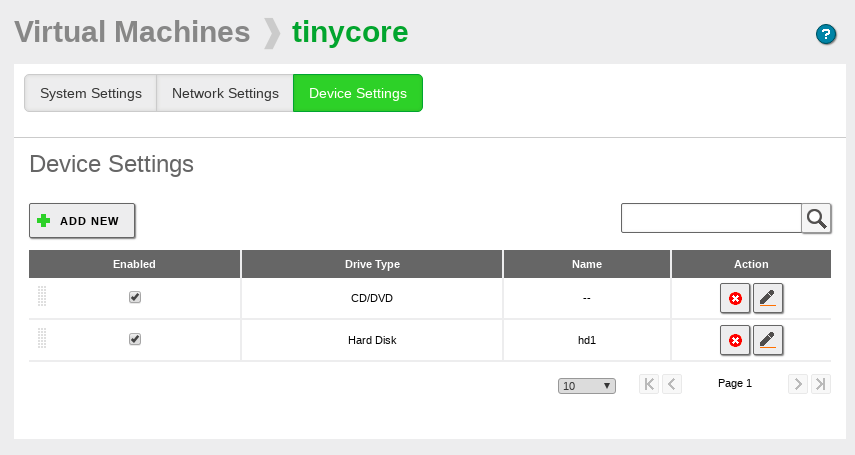
Device Settings
It contains the list of storage drives associated with the machine. You can associate CDs or DVDs (providing the path to an ISO image), and also hard drives. For the hard drives, you can also provide a image file of either KVM or VirtualBox, or just specify the size in megabytes and an identifier name and Zentyal will create the new empty disk. By unchecking the checkbox Enabled, you can temporally disconnect any of the drives without deleting them.
Virtual machine maintenance¶
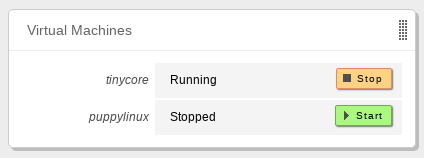
In the you have a widget that contains the list of virtual machines and their current state (running or not), and a button that allows you to Stop or Start them if you want to.
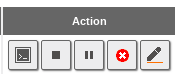
In the section you can see, from left to right, the following actions you can execute over a machine:
Besides the delete and edit buttons, you can carry out the following actions:
View Console
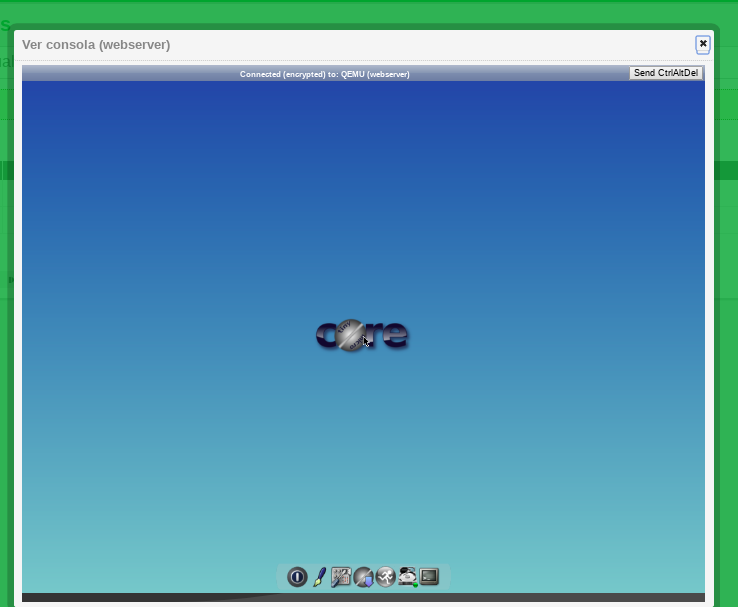
It will open a pop-up window where you can access to the terminal of the virtual machine, using the VNC protocol.
Start/Stop
It allows you to start or stop the machine, depending on its current state. In case the machine is in ‘Pause’ state, the ‘start button’ will resume execution.
Pause/Continue
From here you can pause the execution of the machine while it is running, without losing the running state. Once the machine is pause, you can click the same button to resume execution.
At the top left you can also see an indicator that be either red, yellow or green depending whether the machine is stopped, paused or running.
An example of a machine using VNC: