Routing¶
Configuring routing with Zentyal¶
Gateway¶
The gateway is the host used to start the route for the connections associated with a destination that is not in the local network. This means that if the system does not have static routes defined or if none of these match with the desired transmission, the default gateway will receive the traffic.
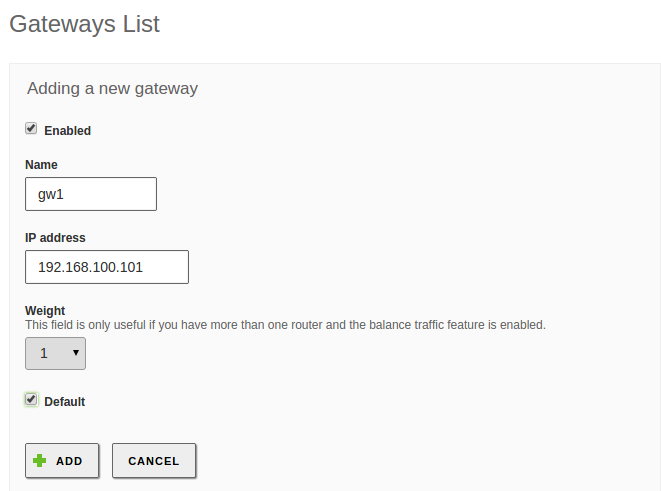
To configure a gateway in Zentyal go to , which contains the following parameters.
- Enabled:
- Indicates whether this gateway is effectively working or if it is disabled.
- Name:
- Name used to identify the Gateway.
- IP Address:
- IP Address of the gateway. This address has to be directly accessible from the host Zentyal is installed on, this means, without other routers in the middle.
- Weight:
- The heavier the weight, more traffic will be sent using this gateway if you have traffic balancing enabled. For example, if the first gateway has a weight of ‘7’ and the second one has a weight of ‘3’, 7 bandwidth units will go through the first one per each 3 bandwidth units that go through the second one, in other words, 70% of the traffic will use the first gateway and the remaining 30% will use the other one.
- Default:
- If this option is enabled, this will be the default gateway.
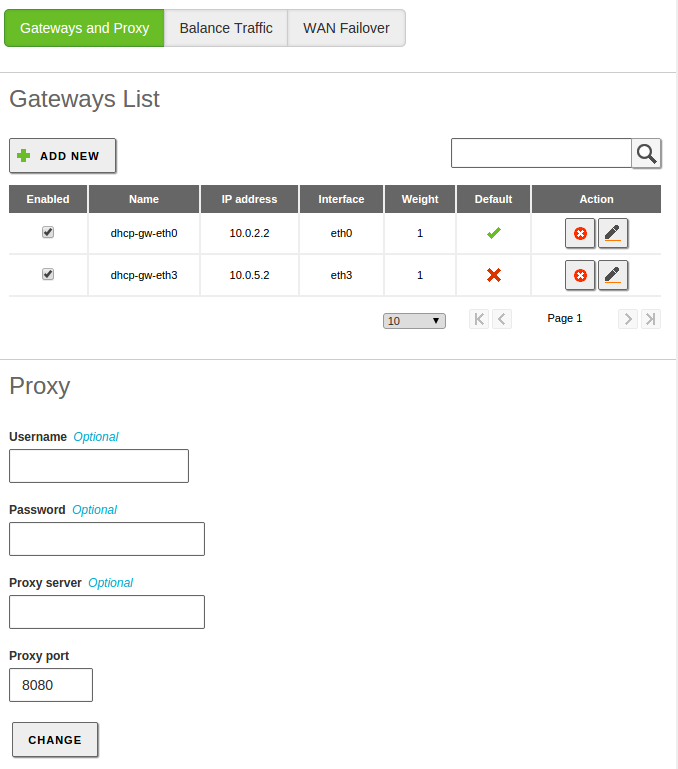
If you have configured interfaces as DHCP or PPPoE [1] you can not add a gateway explicitly for these, because they are automatically managed. Nevertheless, you can still enable or disable them by editing the Weight or choosing whether one of them is the Default, but it is not possible to edit any other attributes.
Additionally Zentyal may need a proxy in order to access the Internet, for example, for software and antivirus updates, or for HTTP proxy re-direction.
In order to configure this external proxy, go to . Here you can specify the address for the Proxy server and also the Proxy port. A User and Password can be specified if the proxy requires them.
| [1] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PPPoE |
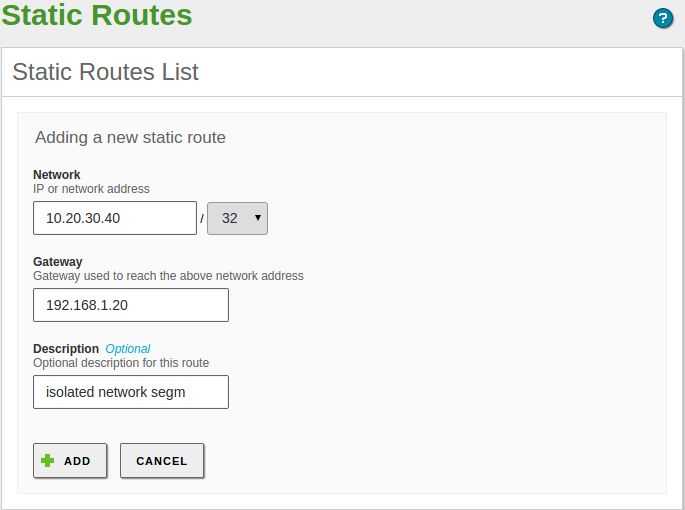
Static route table¶
If all the traffic directed to a network must go through a specific gateway, a static gateway is added.
For making a manual configuration of a static route, you have to use .
These routes can be overwritten if the DHCP protocol is in use.
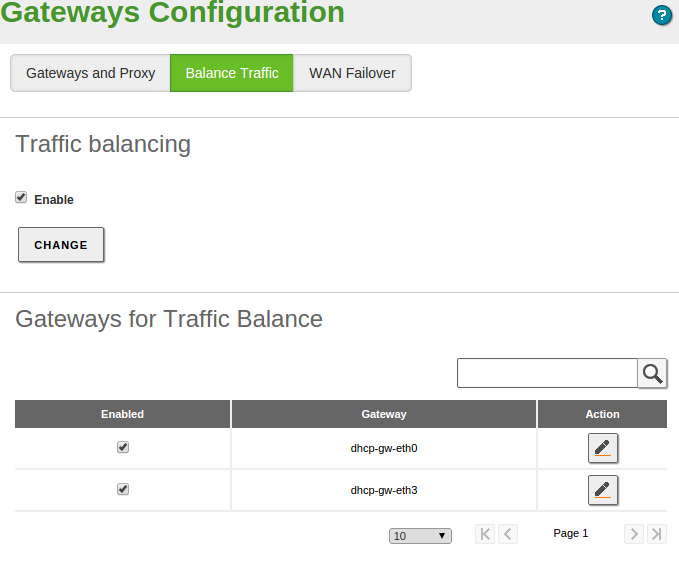
Configuring traffic balancing with Zentyal¶
As mentioned previously, a single host can have more than one configured gateway, which leads to a situation where new parameters need to be taken into account during the configuration of a Zentyal server.
The routing rules for more than one gateway, also known as multigateway rules, allow the network to use multiple connections to the Internet, in a transparent way. This can be very useful for organisations that require more bandwidth than can be offered by a single line - or that can not tolerate interruptions to Internet access, which is very common nowadays.
Traffic balancing shares the outgoing connections to the Internet in a distributed way, allowing complete use of the available bandwidth. The simplest configuration is to establish the different weights for each gateway - so that if the connections have different capacities, you can guarantee optimal use. Bear in mind that connection is the minimal unit for balancing. Packets belonging to a same connection are not going to be balanced among different gateways.
Tip
As a rule of thumb to have an approximate estimation of the traffic that is going to travel though each gateway, you can calculate the sum of the weights and the percentage of each weight over the total. For example, if you have 3 gateways, the first one with weight 3, the second with weight 7 and the third with weight 10, the total is 20. You will have 3/20 of the traffic on the first gateway, 7/20 on the second and half of the traffic on the third, 10/20.
Tip
Not all the gateways have to be used for the balancing. You can set aside one of the gateways for videoconferencing, for example.
Additionally, Zentyal can be configured to always send given types of traffic through a specific router as needed. A common example is to always send e-mail traffic or all the traffic from a pre-determined subnet, through a specific router.
Multigateway rules and balancing can be established in the section , Traffic balancing tab. In this section rules can be added to ensure certain connections are routed though a specific gateway, depending on the Interface, the Source (it can be an IP address, one Object, the Zentyal server itself or Any), the destination (an IP address or an Object), the Service to which you want to associate this rule and the Gateway to where the specified traffic should be routed.