Printers sharing service¶
About the printers sharing service¶
For the management of printers and their access permissions, Zentyal integrates Samba, as described in the Configuring a file server with Zentyal section. As a printing system, in coordination with Samba, Zentyal integrates CUPS [1] (Common Unix Printing System).
| [1] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Common_Unix_Printing_System |
Printer server configuration with Zentyal¶
In order to share a printer in your network and allowing or denying users and groups access, you need to have access to a printer from a host running Zentyal. This can be done through direct connection, parallel port, USB or through the local network. Besides that, you will need to know the following information; the manufacturer, the model and the driver a printer uses in order to obtain good results during operation.
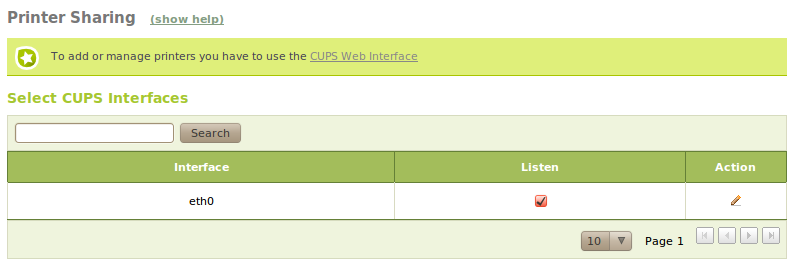
First, it is worth noting that the configuration and maintenance of printers is not through the Zentyal interface but from the CUPS interface. If you manage the Zentyal server locally then you do not need to do anything special, but if you want to give access to other machines on the network you must explicitly allow access to the network interface, as by default, CUPS will not listen to it for security reasons.
The CUPS management port is by default 631 and you can access the management interface by using the HTTPS protocol via the network interface on which you have enabled CUPS to listen to. Localhost can be used if you are operating directly on the Zentyal host.
https://zentyal_address:631/admin
For convenience, if you are using the Zentyal interface, you can access CUPS directly through the CUPS web interface link.
For the authentication use the same username and password with which you use to access the Zentyal interface.
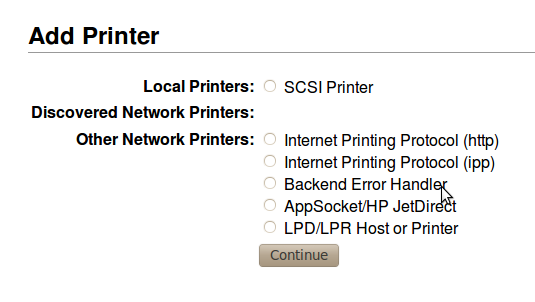
Once you have logged onto the CUPS administration interface, you can add a new printer through Printers ‣ Add printer.
The first step of the wizard used to add a new printer is, select the type of printer. This method depends on the printer model and how it is connected to your network. CUPS also provides a feature for the automatic discovery of printers. Therefore, in most cases it is possible that your printer is automatically detected thus making the configuration easier.
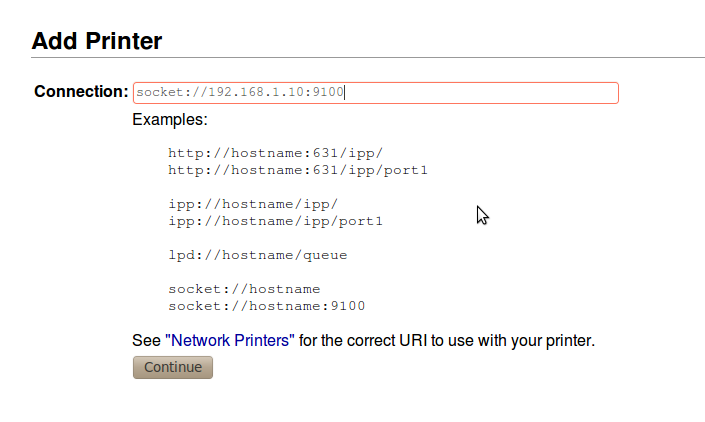
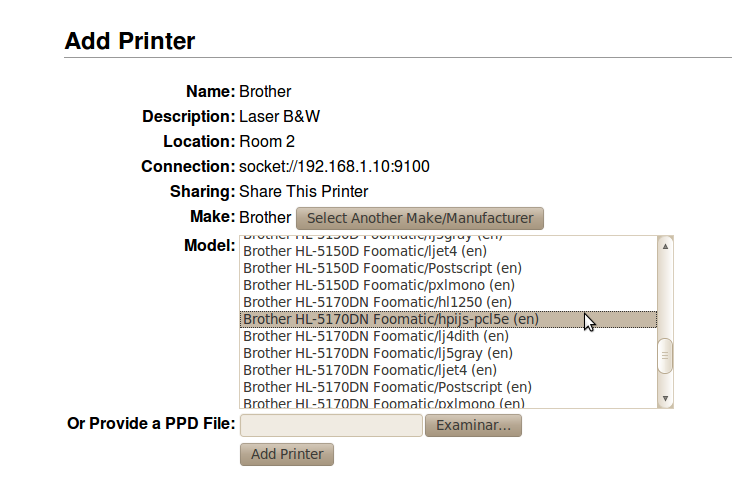
Depending on the method you have selected, you might need to configure the connection parameters. For example, for a network printer, you must establish the IP address and the port as shown in the image.
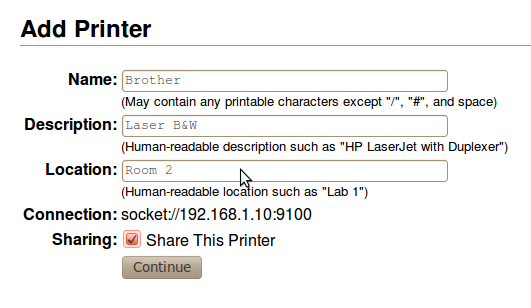
In the next step, you can specify the printer’s name that will be used to identify it later on, together with other additional descriptions of its features and placement. These descriptions can be any character string and their value will be only informational. On the other hand, the name can not include spaces nor special characters.
Later, you must set the manufacturer, model and which printer driver to use. Once you have selected the manufacturer, a list of available models will appear, with different drivers for each model on the right, separated by a slash. You also have the option to upload a PPD file provided by the manufacturer, if your printer model does not appear on the list.
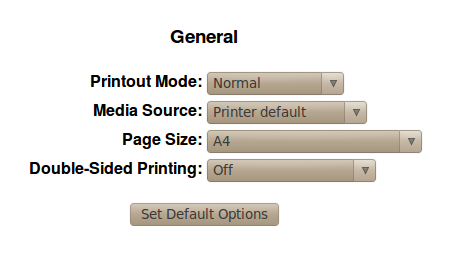
Finally, you will have the option to modify the general settings.
Once you have completed the wizard, your printer will be configured. You can check which printing jobs are pending or on progress through Jobs ‣ Manage jobs within the CUPS interface. You can perform many other actions, such as print a test page. For more information about printer management with CUPS it is recommended to read the official documentation [3].
| [3] | http://www.cups.org/documentation.php |
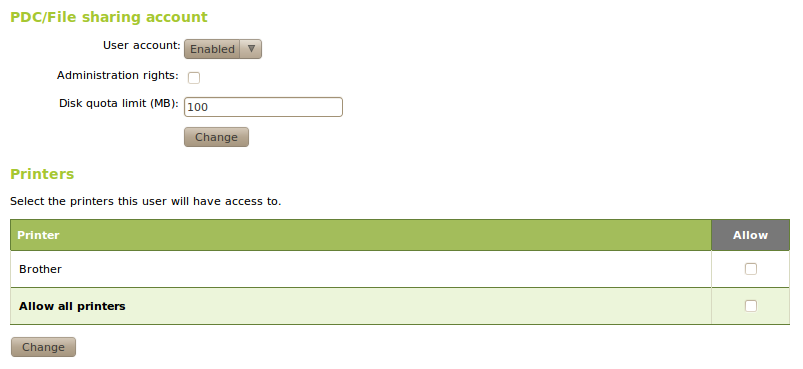
Once the printer has been added through CUPS, Zentyal can export it by using Samba.
Once the service is enable and changes are saved, you can start allowing access to these resources by editing groups or users (Groups ‣ Edit Group ‣ Printers o Users ‣ Edit User ‣ Printers).