First steps with Zentyal¶
Administrative web interface of Zentyal¶
Once you have installed Zentyal, you can access to the administrative web interface of Zentyal both through its own graphical environment included in the installer and from anywhere on the internal network, using the address: https://ip_address/, where ip_address is the IP address or the hostname on which Zentyal is installed. Because access is through HTTPS, the first time it is accessed the browser will ask you whether you trust the site. You simply accept the self-generated certificate.
Warning
To access to the web interface, you must use Mozilla Firefox. Please note that other browsers such as Microsoft Internet Explorer are not supported.
The first screen asks for the username and password. The user created during the installation and any other user of the admin group can authenticate as administrator.
Login
Once authenticated, you will see the administrative interface, this is divided in three main parts:
- Left side menu:
- Contains links to all the services that can be configured by using Zentyal, separated into categories. When you select a service in this menu, a sub menu might appear to configure a particular requirement in the selected service.
Side menu
- Top menu:
- Contains actions: save the changes made in the contents to ensure the changes are effective, and log out.
- Main content:
- The content that occupies the central part, consists of one or more forms or tables with information about service configuration that are selected through the left side menu and its sub menus. Sometimes, in the top, you can see a bar with tabs: each tab represents a different subsection within the section you have accessed.
Dashboard¶
Dashboard is the initial interface screen. It contains a series of widgets that can be configured. You can reorganise the widgets at all times by clicking on their titles and dragging them.
By clicking on Configure Widgets the interface changes, allowing you to remove and add new widgets. To add a new widget, you need to search for it using the top menu and drag it to the central section. To remove a widget, click on the X in the upper right corner of the window.
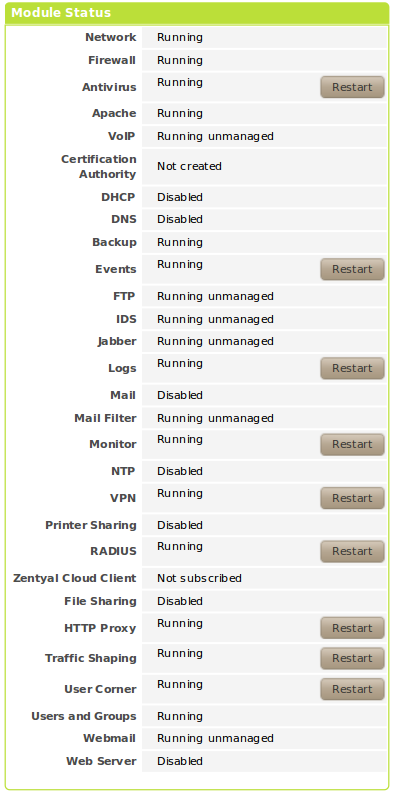
One of the important widgets in the Dashboard displays the status of all modules installed on Zentyal.
The image shows the status of a service and the action you can carry out for this service. The different statuses are:
- Running:
- The service is running and listening to client connections. You can restart a service using Restart.
- Running unmanaged:
- If you haven’t enabled the module yet, it will be running with the default configuration set by the distribution.
- Stopped:
- The service is stopped either because the administrator has stopped it or because a problem has occurred. You can restart the service by clicking on Restart.
- Disabled:
- The module has been explicitly disabled by the administrator.
Configuration of the module status¶
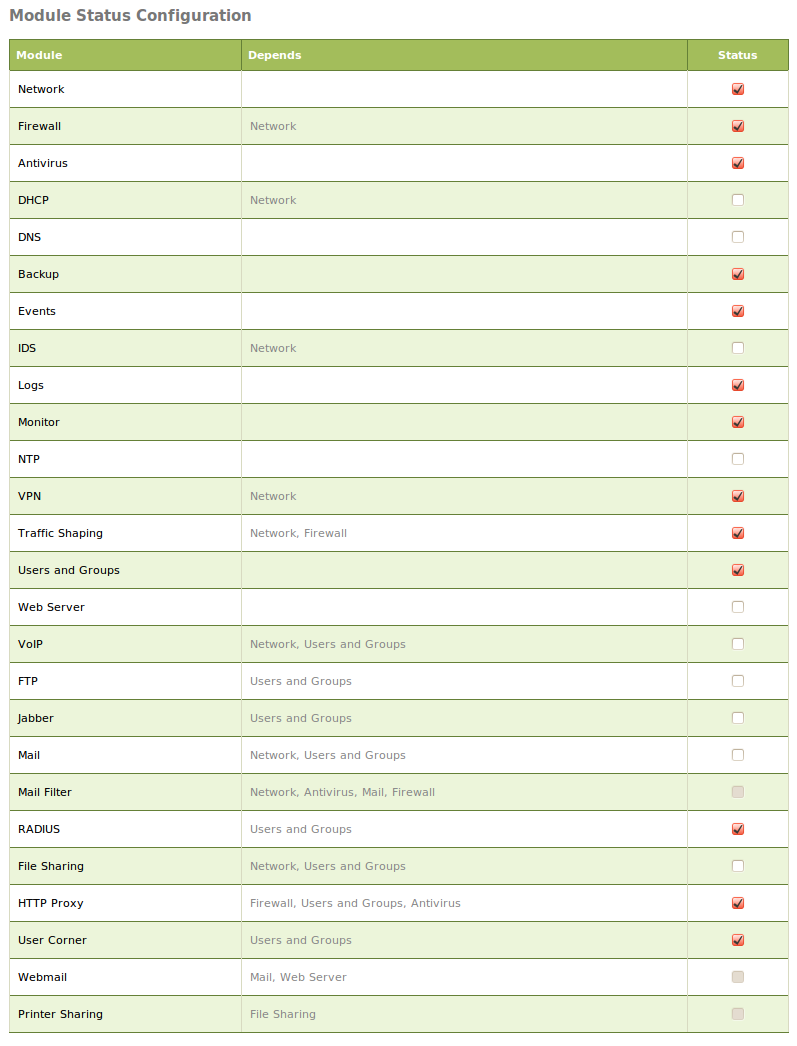
Zentyal uses a modular design in which each module manages a different service. To configure each of these services you must enable the corresponding module from Module Status. All those functions that have been selected during the installation will be enabled automatically.
Each module may have dependencies on others modules in order to work. For instance, DHCP module needs to have the network module enabled so that it can serve IP addresses through the configured network interfaces. The dependencies are shown in the Depends column and until these are enabled, you can’t enable the module.
The first time you enable a module, you are asked to accept the set of actions that will be carried out and configuration files that will be overwritten. After you have accepted all the actions and listed files, you must save changes in order to apply the configuration.
Applying the configuration changes¶
An important feature to consider when working with Zentyal is the way configuration changes are applied when made through the interface. Initially, changes must be accepted in the form, then to make these changes effective and apply them permanently you must click on Save Changes in the top menu. This button will change to red if there are any unsaved changes. Failure to follow this procedure will result in the loss of all changes made during the session once you end it. An exception to this rule is the users and groups management: here the changes are applied directly.
Warning
If you change the network interface configurations, firewall or administrative interface port, you might loose the connection. If this is the case you should change the URL in the browser or reconfigure through the local GUI.
General configuration¶
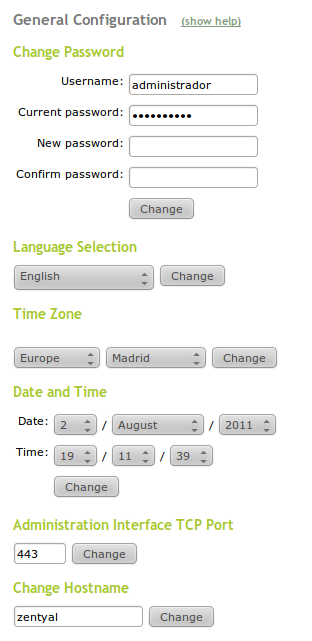
There are several parameters in the general configuration of Zentyal that can be modified in System ‣ General.
- Password:
- You can change the password of an user. It is necessary to introduce
- his/her Username, Current password, New password and to confirm the password again in the Change password section.
- Language:
- You can change the interface language using Select a language.
- Time Zone:
- You can specify city and country to adjust your time zone offset.
- Date and Time
- You can specify the date and time for the server, as long as you are not synchronizing automatically with an external NTP server.
- Administrative interface port:
- By default, it is the HTTPS port 443, but if you want to use it for the web server, you must change it to another port and specify it in the URL when you access https://ip_address:port/.
- Hostname:
- It is possible to change the hostname or the hostname, for example zentyal.home.lan. The hostname is helpful so the server can be identified from other hosts in the same network.
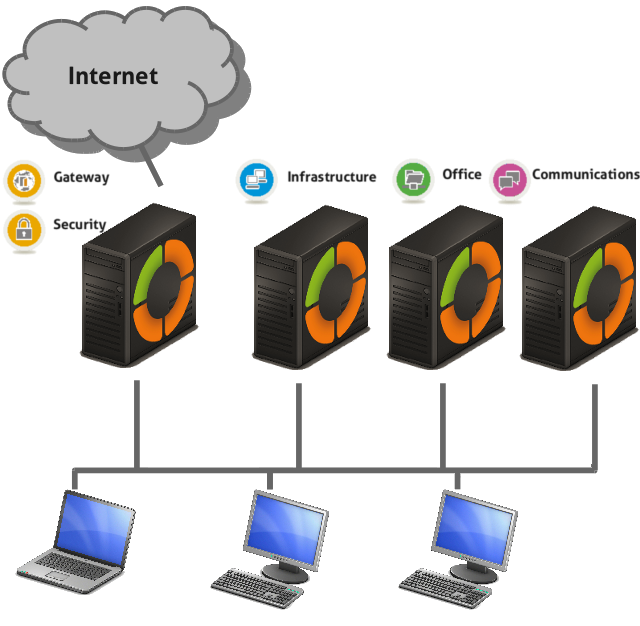
Location in a Zentyal network¶
Zentyal can be used in two fundamental ways:
- gateway and firewall for Internet connection,
- server for network (local or Internet) services.
You can decide to install everything on a single host or to separate the different services into several hosts, depending on the requirement characteristics of each deployment.
The image Locations in the network shows the different locations a Zentyal server can take within a network, both working as a link between networks or as a server within the network itself.
In this documentation you will find out how to configure Zentyal as a gateway and firewall. And of course you will also see how to configure Zentyal when it acts as another server within a network.
Network configuration with Zentyal¶
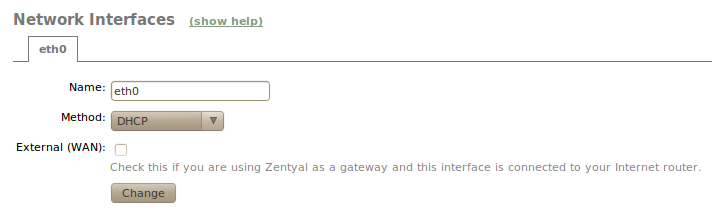
Through Network ‣ Interfaces you can access the configuration of each network card detected by the system and you can select between a static configuration (manually configured), dynamic (DHCP configuration), VLAN (802.1Q) trunk, PPoE or bridged.
In addition, you can define each interface to be External if it is connected to an external network, such as the Internet, in order to apply stricter firewall policies. If you don’t do this, the interface is considered internal, connected to a local network.
When you configure an interface to serve DHCP, not only do you configure the IP address, but also the DNS servers and gateway. This is usual for hosts within the local network or for external interfaces connected to the ADSL routers.
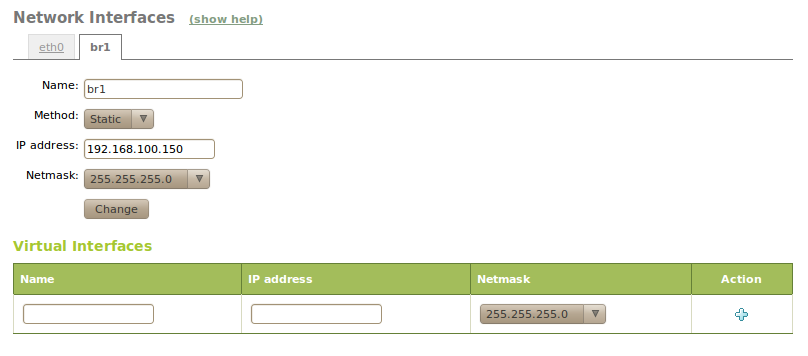
If you decide to configure a static interface you must specify the IP address and the network mask. You can also associate one or more Virtual Interface to this real interface to use additional IP addresses.
These additional addresses are useful to provide a service in more than one IP address or sub-network, to facilitate the migration from a previous scenario or to have a web server with different domains using SSL certificates.
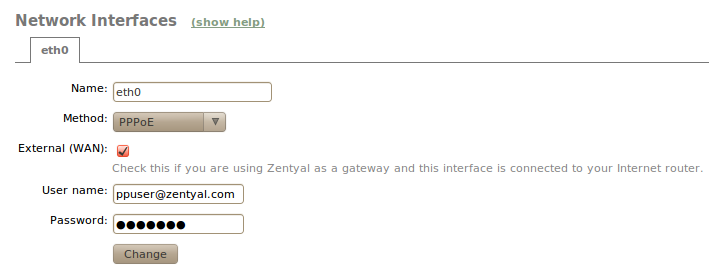
If you use an ADSL router PPPoE [1] (a connection method used by some Internet providers), you can also configure these types of connections. To do this, you only have to select PPPoE and introduce the Username and Password supplied by your provider.
If you connect the server to one or more VLAN networks, select Trunk (802.11q). Once selected, using this method you can create as many interfaces associated to the defined tag as you wish and consider them as if they were real interfaces.
The VLAN network infrastructure allows you to segment the local network to improve performance and security, without the need to invest in hardware that would usually be necessary to create each segment.
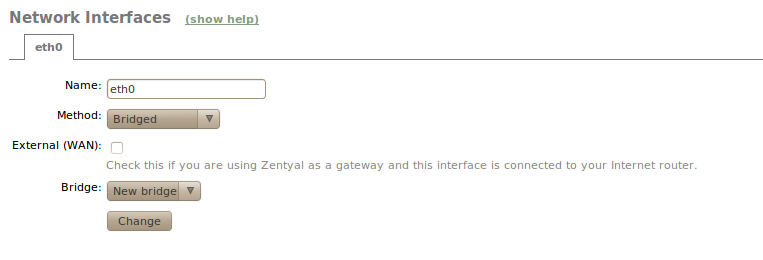
The bridged mode consists of associating two physical network interfaces attached to your server that are connected to two different networks. For example, one card connected to the router and another card connected to the local network. By using this association you can redirect the network traffic transparently from one card to the other.
The main advantage here, is that client configurations do not need changing when the Zentyal server gateway is deployed. Traffic that passes through the server can be managed using content filtering or the intrusion detection system.
You can create this association by changing the interface with Bridged network. You can see how by choosing this option for a new Bridged network. You can then choose the group of interfaces you want to associate to this interface.
This will create a new virtual interface bridge which will have its own configuration as well as a real interface and therefore, even the traffic moves through in transparent mode, it can be used to offer other services such as the administrative interface of Zentyal or a file server.
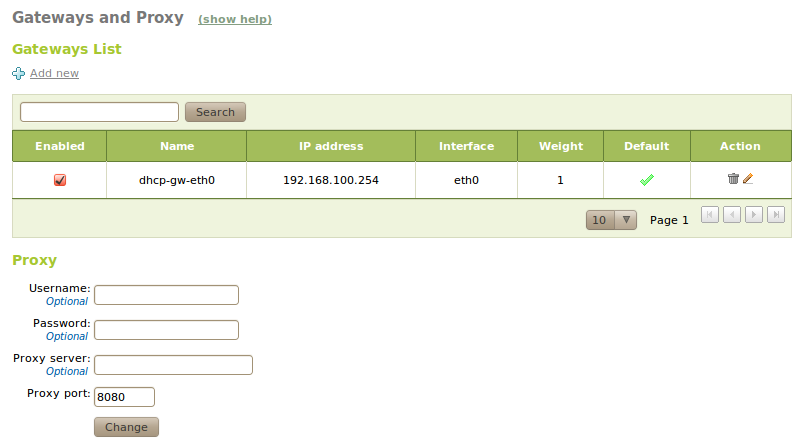
In case you need to configure the network interface manually, define the gateway to Internet using Network ‣ Gateways. Normally this is automatic if DHCP or PPPoE is in use, but not in all other cases. For each gateway you can indicate the Name, IP address, Interface to which it is connected. The Weight defines the priority compared with other gateways and whether it is Predetermined by all of them.
In addition, if an HTTP proxy is required for Internet access, you can also configure this in this section. This proxy will be used by Zentyal for connections, such as update and installation of packages or update of the anti-virus data files.
To allow the system to resolve domain names, you must indicate the address of one or several name servers in Network ‣ DNS.
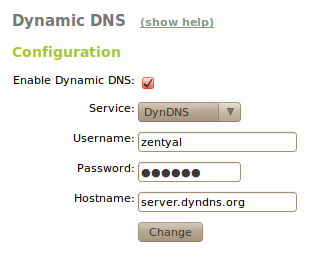
If the Internet connection assigns a dynamic IP address and you need a domain name to re-direct, you need a provider of dynamic DNS. By using Zentyal you can configure some of the most popular providers of dynamic DNS.
To do this, you must select Network ‣ DynDNS where you can choose the Service provider, Username, Password and Hostname which needs updating when the public address changes. Finally select Enable dynamic DNS.
Zentyal connects to a provider to obtain a public IP address avoiding any translation of the network address (NAT) between the server and Internet. If you are using this feature in the multirouter [2] scenario, you must not forget to create a rule to ensure the connections to the provider always use the same gateway.
| [1] | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PPPoE |
| [2] | Check Configuring traffic balancing with Zentyal for more details. |
Network diagnosis¶
To check that the network has been configured correctly, you can use the tools available in Network ‣ Diagnosis.
Ping is a tool that uses the ICMP network diagnosis protocol to observe whether a particular remote host is reachable by means of a simple “echo request”.
You can also use the traceroute tool that is used to determine the route taken by packages across different networks until they reach a given remote host.
Also, you can use the domain name resolution tool, which is used to verify the correct functioning of the name service.